Working in healthcare has never been easy, but nowdays the job feels heavier than ever. Clinics and hospitals are stretched thin. Staff shortages are everywhere – patients need more care, more nurses and doctors are burning out or retiring, and the demand for healthcare keeps climbing faster than the workforce can keep up.
- 28% of clinicians say they don’t have enough time to deliver proper care.
- 69% are seeing more patients than two years ago.
- Nearly half admit that fatigue is hurting the quality of their work.
Add to that the paperwork. Anyone who’s worked in a hospital knows the drill: you spend almost as much time typing as you do treating. On average, healthcare professionals sink 13.5 hours a week into documentation – a third of their working hours. Nurses hit 16.5 hours, doctors about 15. And much of it doesn’t even fit into the shift. An extra 3.2 hours a week gets done at home, often late at night, after already gruelling days. During patient visits, time is divided between the patient and the EHR.
No wonder burnout is so widespread. By 2024, 43.2% of U.S. physicians reported feeling burned out. It is not surprising that at some point, many begin to feel less like doctors and more like archivists.
This is where AI begins to show real promise, not as hype, but as a lifeline. AI tools can automate significant portions of the documentation process – from structuring notes to flagging errors and extracting patterns. AI gives clinicians precious time to do what drew them to medicine in the first place: caring for people.
Key AI in healthcare statistics you need to know
AI isn’t some far-off idea anymore – it’s already reshaping how healthcare runs, from the ER to the pharmacy counter. And the numbers behind this shift make it clear: the adoption wave is building fast.
- 85% of healthcare leaders – from payers to health systems to tech providers – say they’ve already dipped into generative AI or are actively rolling it out. It’s not just pilots anymore; it’s real-world deployment, and that changes what frontline teams will be working with every single day.
- On the ground, 80% of U.S. hospitals are already using AI to sharpen patient care and streamline workflows. That means everything from faster triage to smoother discharge planning – areas where every wasted minute translates into stress for staff and risk for patients.
- The business side is catching up just as quickly. The AI healthcare market hit $32.34 billion in 2024 and is expected to skyrocket to $431 billion by 2032. Translation? Budgets are shifting, investments are flowing, and the tools you’ll be handed in the next few years are going to look radically different from the ones you’ve relied on.
- 43% of healthcare leaders say they’re already using AI for in-hospital patient monitoring. That’s ICU dashboards, remote telemetry, and predictive alerts – things that can help staff get ahead of a crisis instead of chasing it after the fact.
Patients themselves are split. 80% of younger adults (18–34) are open to AI in their care, but fewer than 60% of those over 55 trust it. For providers, this means every AI-driven encounter is a balancing act between efficiency and building trust with patients, who may not be ready to let a machine have a say in their health.
Inside organizations, adoption is accelerating:
- 94% of providers see AI as “core” to operations.
- 86% report extensive use in scheduling, pharmacy workflows, and oncology.
- 41% have AI handling parts of patient conversations. That’s a huge cultural shift in how care is delivered.
And yet, despite this momentum, healthcare still trails other industries in AI adoption. The World Economic Forum calls it “below average” in AI adoption. Why? Because medicine carries a weight most industries don’t – the ethical stakes, the privacy risks, the life-or-death consequences. Rolling out AI in healthcare isn’t just about pushing efficiency; it’s about threading the needle between innovation and responsibility. And that’s exactly where the tension, and the opportunity, lies
The positive impact of AI in healthcare
AI is not just a tool – it’s a force multiplier for clinicians, nurses, and hospital staff.
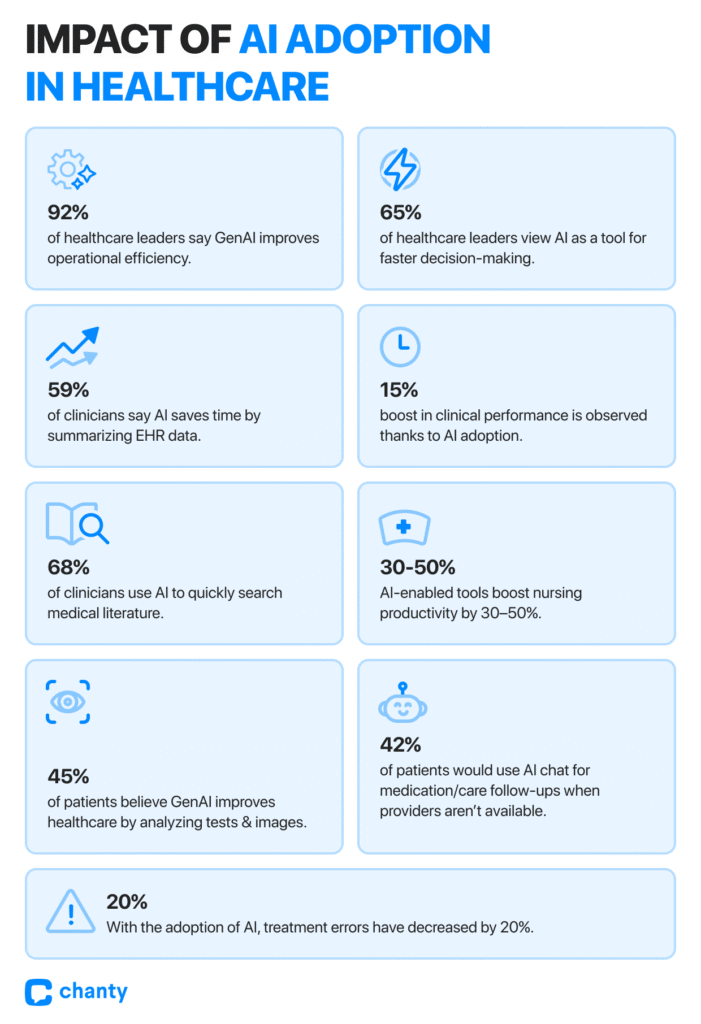
- 92% of healthcare leaders believe Generative AI improves operational efficiency, while 65% see it as a tool for faster decision-making. That’s not just boardroom talk – it’s about giving staff time back in their day, helping them make informed decisions faster, and reducing the cognitive burden of juggling countless patient details.
- Clinicians using AI-powered decision-support systems report a 20% decrease in treatment errors while improving performance by 15%.
This shows AI doesn’t just save time; it enhances the effectiveness of the people on the frontlines, making the system safer for patients and less stressful for staff. - 59% of clinicians say AI can save time by summarizing patient data from EHRs, while 68% report that GenAI helps by quickly searching medical literature.
- According to Dr. Angela Spatharou, Partner at McKinsey & Company, AI has enormous potential to boost productivity, efficiency, and sustainability in health systems – but more importantly, it lets practitioners spend more time in direct patient care. Think about that: fewer hours lost to repetitive tasks, more moments actually connecting with patients. That’s what healthcare professionals wanted all along.
In nursing, AI-enabled tools have been reported to increase productivity by 30–50%, reducing manual calculations and burnout while freeing energy for complex care decisions.
Patients notice the benefits too.
- Nearly half of Americans (45%) say GenAI can improve healthcare by analyzing medical tests, X-rays, and images more thoroughly.
- Over 42% would even use it for follow-up questions about medications or care when a pharmacist or clinician isn’t available. For staff, this means fewer repetitive queries and a more empowered patient population – freeing up time for the critical tasks only a trained professional can handle.
Some of the clearest examples come from cutting-edge research. Massachusetts General Hospital and MIT developed AI algorithms specifically for radiology applications. The system achieved a remarkable 94% accuracy rate in detecting lung nodules, far outperforming human radiologists, who scored 65% on the same task. This not only boosts diagnostic reliability but also allows radiologists to focus on complex cases and personalized patient care, instead of routine screenings.
Patient engagement in the age of AI
Getting a patient’s attention today is like fighting for scarce currency. Nobody wants to waste hours in a waiting room or repeat the same health history ten times. People demand care that feels fast, personal, and convenient – and they’re choosing providers who deliver exactly that.
- 1 in 4 Americans now say they won’t even pick a provider who refuses to adopt AI. That’s not a side preference anymore – that’s a dealbreaker.
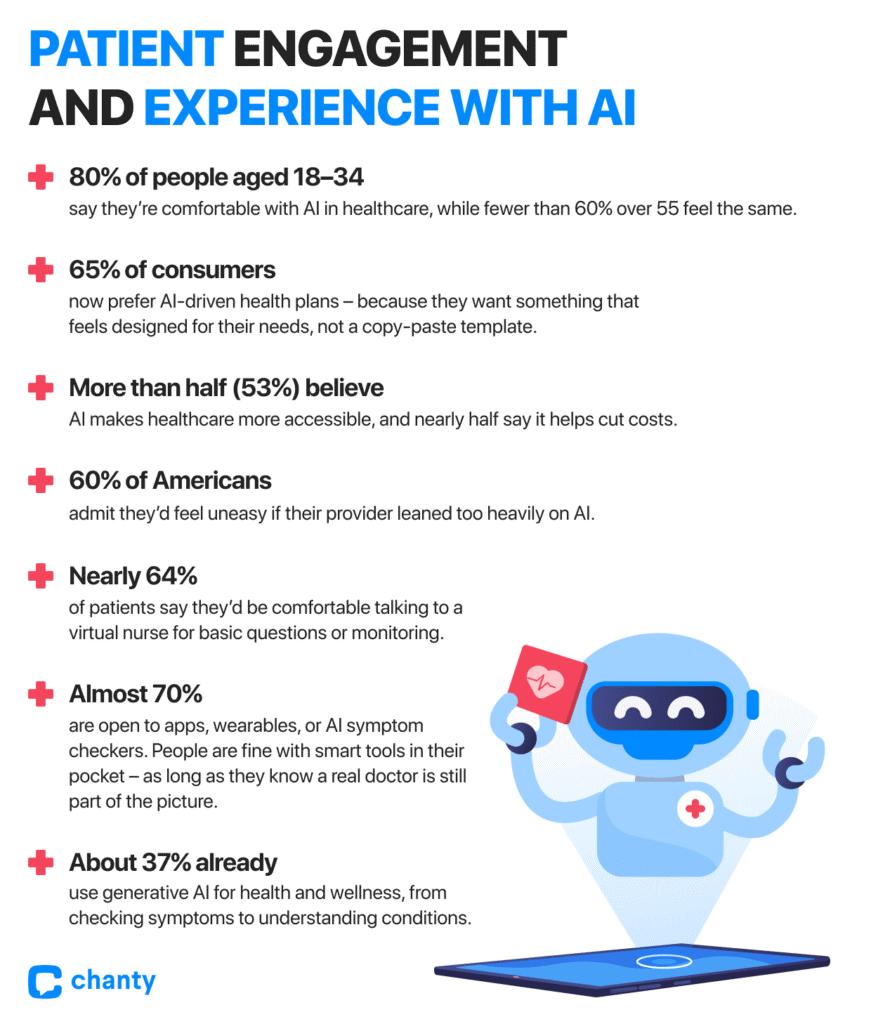
- 65% of consumers now prefer AI-driven health plans – because they want something that feels designed for their needs, not a copy-paste template.
- 53% believe AI makes healthcare more accessible, and nearly half say it helps cut costs. For many, these benefits are the difference between putting off treatment and finally getting it.
Generational divides matter here too: 8 out of 10 people aged 18–34 say they’re comfortable with AI in healthcare, while fewer than 6 in 10 over 55 feel the same. The message? A whole generation expects tech-driven care, and if you can’t meet them there, they’ll find someone who will.
Still, the trust gap is real.
- A majority – 60% of Americans – admit they’d feel uneasy if their provider leaned too heavily on AI. But the nuance here matters: patients aren’t against the technology itself – they just don’t want it replacing the human side of care. When AI is framed as a helper, the story changes.
- Nearly two-thirds (64%) of patients say they’d be comfortable talking to a virtual nurse for basic questions or monitoring.
- Almost 70% are open to apps, wearables, or AI symptom checkers. People are fine with smart tools in their pocket – as long as they know a real doctor is still part of the picture.
And let’s be honest: patients aren’t waiting for the healthcare system to catch up. About 37% already use generative AI for health and wellness, from checking symptoms to understanding conditions. One in five do it specifically to learn about their own medical situation. The demand is there, whether providers are ready or not. This way, the real danger for providers isn’t in adopting AI too quickly. It’s in falling behind while patients move forward.
AI adoption in healthcare communication and collaboration
Artificial intelligence is no longer just about detecting diseases or crunching numbers; it’s creeping into the daily conversations that keep healthcare running. From the way doctors answer the patients’ questions in the portal to how nurses hand off cases during a shift change, AI is starting to shape communication itself. And a system where miscommunication is one of the top causes of medical errors, this shift matters.
How AI was adopted for the medical communications
The numbers show just how fast things are moving. In 2024, the American Medical Association reported that 66% of U.S. physicians were already using AI, up from just 38% the year before. One in five was applying it to the least glamorous but most time-consuming part of the job: documentation – charting, visit notes, billing codes. These aren’t just clerical tasks; they directly affect how accurately information passes from one professional to another.
The Medical Group Management Association found that 71% of clinics were using AI in at least some patient visits. Most weren’t fully automated yet – nearly half said they applied AI in up to a quarter of cases. That may sound small, but in practice, it means thousands of messages, notes, and updates are already being filtered or drafted by algorithms every day.
Globally, adoption is accelerating even faster. Elsevier’s Clinician of the Future Report 2025 found that 48% of clinicians worldwide had used AI tools in their work, nearly doubling from 26% in 2024. That kind of jump in just 12 months shows how quickly the technology is becoming part of the communication chain in medicine.
How AI is helping in patient–clinician communication
Communication with patients is often where things break down. Appointments are short, portals are full of messages, and physicians simply don’t have enough hours in the day. AI is starting to plug those gaps.
- Patient portals: At UC San Diego, a 2024 study showed that AI-drafted replies to patient messages were rated more empathetic and higher quality than many physician-written ones. Doctors appreciated the relief from mental fatigue, even if they still edited most drafts before hitting “send.” In other words, AI isn’t replacing the doctor’s voice – it’s giving them a head start.
- Chatbots and assistants: About 10% of physicians using AI rely on patient-facing chatbots for triage, FAQs, or basic self-care advice. Patients like the faster answers but value honesty and easy escalation when a bot can’t handle the issue. Trust improves when the tech is transparent.
- Translation support: Around 14% of physicians now use AI translation tools to connect with patients who don’t share the same first language. In urban hospitals with diverse populations, this isn’t a nice-to-have – it’s often the difference between confusion and safe care.
Impact of AI on interprofessional collaboration
Inside the hospital, AI is quietly tackling another silent problem: communication overload among staff. Clinicians spend a huge portion of their day reading notes, combing through EHRs, and trying not to miss crucial updates.
- Summarization in EHRs: With Epic and Oracle Cerner embedding AI scribes, doctors can now get quick, structured summaries of progress notes and handoffs instead of sifting through pages of text. This not only saves time, but helps cut down on errors that come from information being buried.
- AI scribes in practice: Tools like Nuance DAX Copilot and Nabla Copilot are generating structured consultation summaries in real time. Specialists don’t have to rely on a colleague’s rushed notes – the system captures the essence of the encounter and formats it for clarity.
- Team meeting summaries: Some hospitals are piloting AI-generated summaries of multidisciplinary meetings. Instead of everyone scribbling down their own takeaways, the system produces an agreed-upon record of action points. This reduces repetition and helps teams move faster.
Insights on healthcare cybersecurity risks and the role of AI in data protection
AI is both a shield and a vulnerability in data security. Adoption of AI in healthcare is high, but so is caution:
- Usage: According to report by AMA, 66% of U.S. physicians reported using AI tools in 2024.
- Concerns: Over 60% of healthcare staff worry about transparency, security, and trust.
- Leadership perspective: 72% of healthcare executives list data privacy as the top risk in AI adoption.
- Cyber threat reality: 92% of healthcare organizations faced a cyberattack in the past year, and the average cost of a healthcare data breach now tops $9.77 million.
- Legal literacy gap: Nearly 58.5% of clinicians admit they don’t fully understand the legal obligations tied to AI and PHI.
AI is increasingly integrated into compliance workflows. HIMSS Cybersecurity Surveys show that many hospitals use AI-enabled log monitoring, anomaly detection, and DLP systems to meet HIPAA’s security and privacy requirements. While few public reports break down “what percentage of breaches were prevented by AI,” industry data consistently shows that ML systems accelerate detection and shorten response times.
Real-world examples of AI-linked data exposure
The risks are very real. In 2024, 81.2% of reported large-scale healthcare breaches were due to hacking and IT incidents, each affecting an average of 439,796 records. Several high-profile cases illustrate how AI intersects with PHI security:
- Star Health, India: Hackers used Telegram chatbots to spread millions of leaked medical records – demonstrating how bots can become amplifiers of exposure.
- Serviceaide / Catholic Health, USA: A misconfigured Elasticsearch database exposed nearly 483,000 patient records, showing that AI vendors themselves can become weak links.
- Generative AI misuse: According to Netskope’s 2025 Threat Labs Healthcare report, sensitive patient data – including protected health information (PHI) – is often uploaded into public AI tools that aren’t HIPAA-compliant, exposing both patients and clinicians to risk.
These incidents underline that AI-related risk is often hidden in official breach categories (misconfigurations, insider error, vendor oversight) rather than labeled “AI-related,” even though AI technologies and workflows play a central role.
The double-edged sword of AI in healthcare communications
AI introduces risks, but also offers powerful protections.
Risks introduced by AI:
- More PHI exchange points via third-party LLMs and cloud services.
- Misconfigurations at vendors and partners.
- Human misuse, from accidental uploads to incomplete de-identification.
Protections empowered by AI:
- Anomaly detection: ML-driven SIEM/UEBA tools flag unusual EHR access, such as mass exports or irregular login locations, reducing detection time.
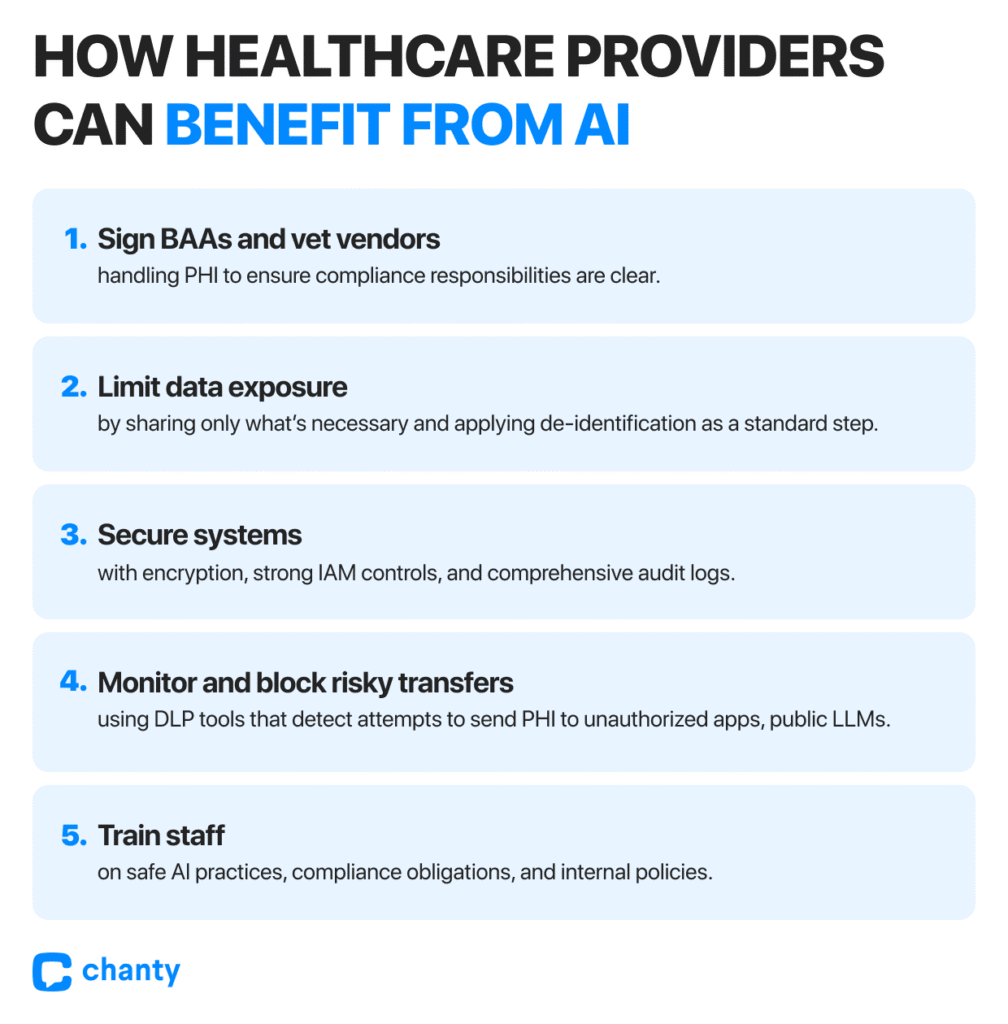
- De-identification in practice: Leading U.S. hospitals now use AI-powered masking tools to anonymize PHI before clinical research, allowing compliance while preserving analytical value.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): AI classifiers tag PHI and automatically block its transfer to unauthorized applications, including public generative AI tools.
- Consent and access automation: AI systems track patient consents and prevent PHI from being routed to unapproved services, reducing administrative overhead.
Regulatory scrutiny and HIPAA alignment
AI in healthcare is now firmly under regulatory attention. U.S. state agencies and the FTC have opened inquiries into AI chatbots, particularly in mental health, citing risks of misinformation and improper data handling. Not all AI models are safe for PHI; using public LLMs like ChatGPT without a signed Business Associate Agreement (BAA) can trigger serious HIPAA violations.
For organizations, HIPAA compliance in the AI era rests on three pillars:
- Contractual: Sign BAAs with any AI vendor handling PHI.
- Technical: Enforce encryption, audit logs, role-based access, and automated safeguards.
- Behavioral: Train staff to avoid uploading PHI into public tools, enforce internal policies, and monitor usage patterns.
Regulators also stress explainability (XAI). If AI-driven recommendations, especially in areas like mental health, cannot be explained, they may raise not just privacy issues but also ethical and legal concerns.
AI is moving fast: two-thirds of physicians already use AI tools, but concern remains equally high, with executives naming privacy as their top risk. Official breach reports logged 133 million compromised patient records in 2023, while in 2024, hacking-driven incidents made up more than 80% of large breaches. Many AI-related factors were hidden under broader labels like “misconfiguration” or “vendor error,” even though AI workflows played a central role.
The way forward is clear: healthcare organizations that treat AI security as a parallel track to AI adoption – embedding safeguards, compliance, and staff training from the start – will not only protect PHI but also maintain patient trust while reaping AI’s benefits in efficiency and care.
The future of AI in healthcare: Access, innovation, and staying human
AI in healthcare is no longer just a futuristic idea. It’s becoming part of the everyday reality for patients and clinicians alike. Today, millions of people are using AI to get preliminary guidance, check symptoms, or even explore possible diagnoses before seeing a doctor. This is especially important for those who face long waiting times for appointments or who live far from healthcare facilities.
On the clinician side, AI is gradually becoming a trusted partner in decision-making. Models like AMIE, trained specifically with clinical data, can generate differential diagnoses (DDx) for hundreds of complex, real-world medical cases. Integrated into interactive interfaces, AMIE helps doctors explore multiple possibilities, organize information faster, and improve diagnostic efficiency. While some imagine a near future where AI could operate fully autonomously, today these systems are tools to enhance human judgment, not replace it. They show enormous potential to reduce errors, improve patient outcomes, and save time–but responsibility and oversight remain essential.
AI also reshapes communication and patient engagement. By summarizing EHR data, drafting messages, or providing translation support, AI helps reduce administrative burdens on clinicians, letting them spend more time with patients. Personalized AI tools – like symptom trackers, AI-assisted health plans, or chatbots – give patients more control and information, making care feel more responsive and connected. At the same time, caution is needed: AI can be overly agreeable or excessively polite, and constant interaction with AI in a mental health context may actually worsen a patient’s state. According to a recent Stanford study, some chatbots can unintentionally reinforce stigma or encourage unsafe behavior. This highlights that AI is a complement to, not a replacement for, trained human specialists, particularly for mental health care.
Looking ahead, AI in healthcare is only going to expand. We’ll likely see deeper integration into clinical workflows, more predictive analytics for preventive care, AI-driven triage that reduces emergency department bottlenecks, and increasingly sophisticated diagnostic support. But with this growth comes ongoing risks: privacy, compliance, and the potential for data exposure must be managed carefully. Real-world incidents – from misconfigured cloud storage to staff uploading PHI to generative AI services – serve as a reminder that innovation carries responsibility.
In the end, AI’s biggest promise lies in making healthcare more accessible, efficient, and patient-centered. It can reach populations who previously struggled to get timely care, help clinicians work smarter, and allow patients to be more actively engaged in their health. But no matter how advanced AI becomes, the best outcomes still depend on real human expertise. AI is a powerful partner in healthcare, capable of transforming the way we diagnose, communicate, and manage health, but it’s not a substitute for living, breathing professionals who understand patients, context, and nuance.